What Is the Upper Heart Made Up of a Short Loop From the Heart to the Lungs and Back Again
Heart is a vital organ that you cannot live without. The role of eye is quite circuitous, only you can understand things better through the eye diagram labeled below. It provides information about different chambers of the centre and valves that help transfer blood from 1 part of your middle to another. Go on reading to learn more almost how your heart works.
Iv Chambers of the Heart and Blood Circulation
The shape of the human heart is like an upside-down pear, weighing between 7-15 ounces, and is little larger than the size of the fist. Information technology is located betwixt the lungs, in the middle of the chest, backside and slightly to the left of the breast bone. The heart, one of the most significant organs in the human body, is a muscular pump, which pumps blood throughout the trunk. Information technology beats approximately 72 times per minute, and pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
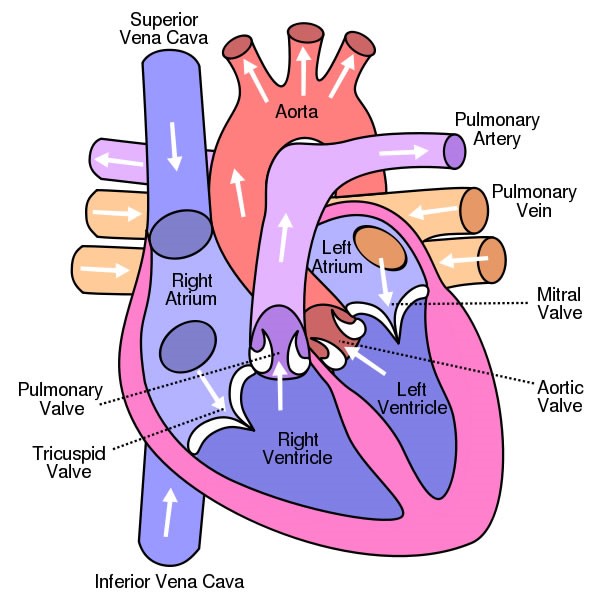
Atria and Ventricles
There are 4 chambers in your heart that are left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, and right ventricle.
- The upper chambers of your center are atria, whereas the lower chambers are ventricles.
- Deoxygenated blood enters your heart through the right atria from where the blood moves into the right ventricle first then to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Your left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs, which is then pumped into the left ventricle from where it moves into the aorta then to the different parts of your body.
Valves to Ensure Unidirectional Blood Flow
Your middle has four types of valves with primary function of regulating the blood menstruation through the heart. Every heart diagram labeledwill conspicuously bear witness these valves. These valves allow blood flow in i management only. Different valves perform different functions.
- Tricuspid valve is located between the right ventricle of your centre and the right atrium, and allows the blood to motility from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
- Pulmonary valve is between the left pulmonary artery of your heart and its right ventricle. Information technology opens up when the right ventricle contracts and allows the blood to move into the left pulmonary artery.
- Similarly, mitral valve has two cusps and is located in a way that it causes a separation between the left ventricle of your heart and the left atrium of your heart. Information technology pumps the oxygenated claret into the left ventricle when the left atrium contracts.
- Aortic valve separates the aorta from the left ventricle and regulate the flow of blood from the ventricle to the rest of your body.
Claret Vessels
- Blood vessels assistance transport blood to-and-fro from your middle. These vessels connect other organs in your body to your eye.
- The basic function of these vessels is to take deoxygenated blood from unlike organs, supply information technology to the heart, and then take oxygenated blood that comes from the lungs into the heart to the rest of your body.
Blood vessels are more than similar a network that helps circulate claret throughout your body. There are 2 types of them: arteries and veins.
- Arteries: These types of blood vessels take oxygen-rich claret from the heart and send to the capillaries. Arteries are quite tough on the exterior but are smooth on the inside. In that location are 3 arteries of the heart, including pulmonary artery, aorta, and coronary arteries. Pulmonary artery is the only artery that takes deoxygenated claret from the right side of your heart to your lungs; aorta is the master avenue of the heart and transports oxygenated blood to the rest of your body; and coronary arteries are fastened to the heart and transfer oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscles.
- Veins: Although they are quite like arteries, they aren't as strong mainly because they don't transport claret at high pressure. The veins receive waste products subsequently the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Three veins of the heart are pulmonary vein, Venae Cavae, and coronary sinus. Pulmonary vein transfer oxygenated blood to the left side of your heart, venae cavae takes deoxygenated blood back to the heart, and coronary sinus receives deoxygenated blood and transfers information technology to the right atria.
The Circulation of Blood
Your circulatory organisation works to transfer oxygenated claret to all the tissues of your torso. Your heart pushes blood out when it contracts. It moves in two cycles. In the systemic loop, controlled by the left side of your eye, the blood circulates in your body and supplies oxygen to your organs, tissues, and other structures. In the pulmonary loop, controlled by the right side of your heart, the blood moves to the lungs to release carbon dioxide and get new oxygen.
In the systemic loop, the oxygenated blood comes from the lungs and enters the left atrium, or the upper left chamber of your heart. The chamber presses on the mitral valve once filled with blood and the blood flows into the left ventricle. The blood on the left side of your center will go into the aorta when the ventricles contract during a heartbeat. The aorta is about an inch wide and supplies oxygen-rich blood to the body's cells. The used blood them moves back and is collected into the two veins, the superior vena cava that receives blood from your upper body, and the junior vena cava that receives blood from your lower body.
These veins empty into the right atrium of your heart from where your blood moves to the correct ventricle through the tricuspid valve. Ventricle contracts and pushes the claret into the pulmonary artery that sends blood to your lungs from where oxygen-rich blood returns to the left ventricle and the process continues.
Outside of the Human Heart
A eye diagram labeled will provide plenty of information about the structure of your middle, including the wall of your heart. The wall of the heart has 3 different layers, such equally the Myocardium, the Epicardium, and the Endocardium. Here's more well-nigh these three layers.
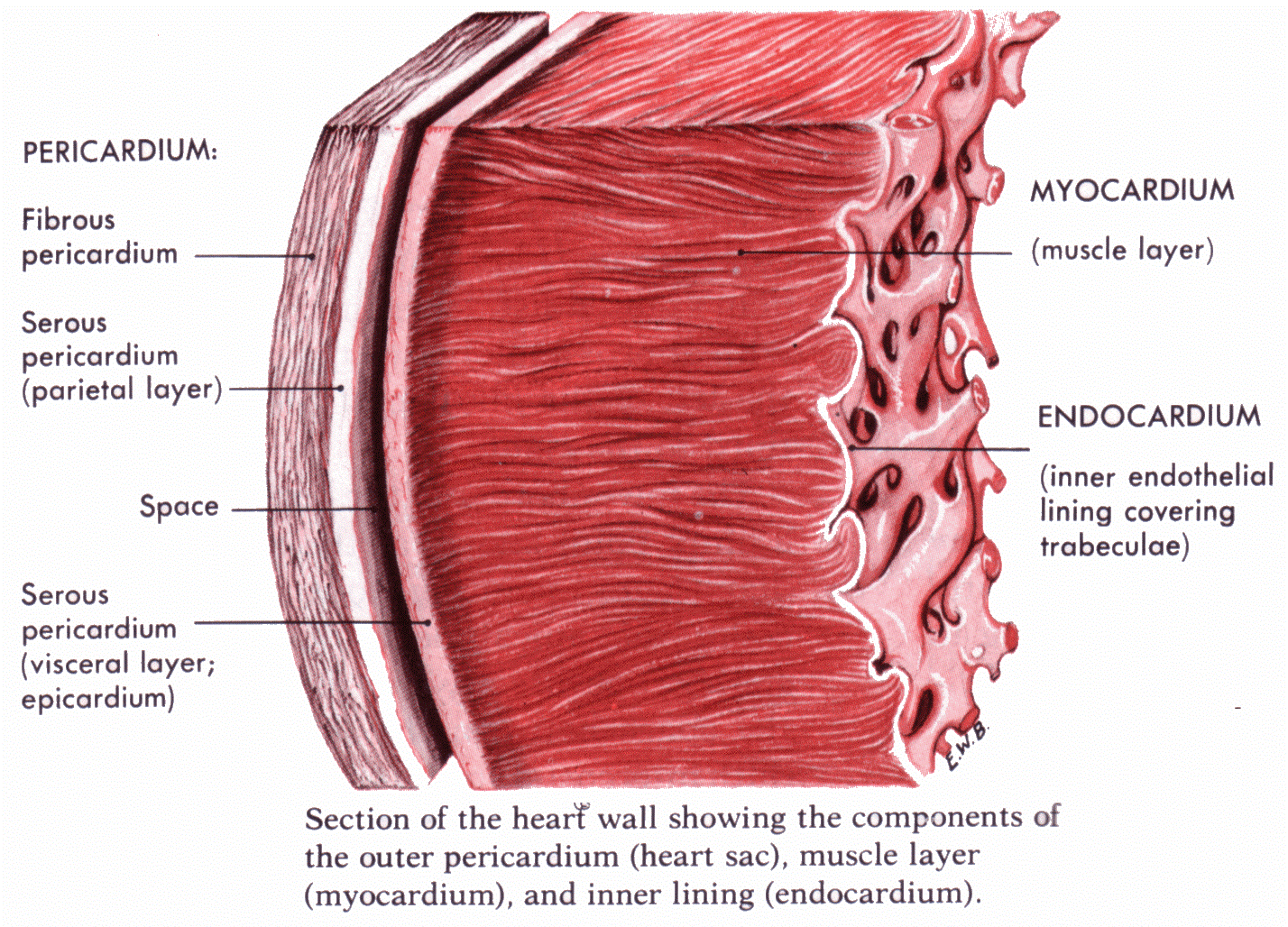
Epicardium
The outermost layer of your heart wall is called the epicardium, which is basically a very thin layer of serous membrane. The membrane provides lubrication and protection to the outer side of your eye, equally y'all can run into in centre diagram labeled.
Myocardium
Right beneath epicardium is some other relatively thicker layer chosen myocardium. This muscular centre layer of heart wall contains cardiac muscle tissue. Most of the thickness and mass of your eye wall is made upwardly of the myocardium. The layer is part of the heart that is pumps blood through your torso.
Endocardium
Nether the myocardium, there is another sparse layer called the endocardium. The layer lines the within of your heart and is normally very polish. The main part of this shine, thin layer is to foreclose your claret from sticking into the sides of your heart. It also helps prevent the formation of deadly blood clots.
Watch this video to learn more about the structure of man heart.
Different Types of Middle Conditions
Coronary Avenue Disease
The arteries that supply claret dorsum to the middle may become clogged due to the buildup of cholesterol plaque. This blockage will crusade coronary avenue affliction. These narrowed arteries may develop a blood clot at any time that leads to a condition chosen center attack.
Myocardial Infarction
Besides called heart attack, myocardial infarction is the outcome of sudden blockage of a coronary artery. The blockage reduces the corporeality of oxygen that gets into your heart, which in plough proves fatal for the eye muscle.
Arrhythmia
The status is characterized by irregular or aberrant heart rhythm acquired by changes in the conduction of electric impulses through your center. Arrhythmias tin be benign or have life-threatening consequences.
Congestive Centre Failure
Yous develop this condition when your heart becomes too stiff or likewise weak to pump enough blood through your torso. If you're noticing symptoms like shortness of breath and leg swelling, this may betoken congestive eye failure.
Myocarditis
Y'all develop this condition when your heart musculus becomes inflamed. In most cases, this inflammation is the event of a viral infection.
Cardiac Abort
Information technology is a type of middle failure because it refers to the sudden loss of function of your heart.
Sudden Cardiac Expiry
When someone dies considering of cardiac abort or sudden loss of heart function, it is called sudden cardiac decease. The condition is sometimes known every bit cardiac arrest.
Heart Valve Disease
You have four valves in your heart and issues with whatever one of them will lead to the development of a heart disease. When non treated early, heart valve disease can pb to the congestive heart failure.
Eye Murmur
When your medico listens to your heartbeat with the help of stethoscope, he may hear abnormal heart audio. This condition is chosen heart murmur, which is generally benign. It may sometimes suggest middle disease equally well.
Source: https://www.newhealthadvisor.org/Heart-Diagram-Labeled.html
0 Response to "What Is the Upper Heart Made Up of a Short Loop From the Heart to the Lungs and Back Again"
Post a Comment